# .NET Core 下的 API 网关

# 网关介绍
网关其实就是将我们写好的API全部放在一个统一的地址暴露在公网,提供访问的一个入口。在 .NET Core下可以使用Ocelot来帮助我们很方便的接入API 网关。与之类似的库还有ProxyKit (opens new window),微软也发布了一个反向代理的库YARP (opens new window)。
关于网关的介绍不多说了,网上文章也挺多的,这些都是不错的选择,听说后期Ocelot将会使用YARP来重写。本篇主要实践一下在.NET Core环境下使用Ocelot。
- Ocelot官网:https://threemammals.com/ocelot (opens new window)
- Ocelot文档:https://ocelot.readthedocs.io (opens new window)
- GitHub:https://github.com/ThreeMammals/Ocelot (opens new window)
- Ocelot资源汇总:https://www.cnblogs.com/shanyou/p/10363360.html (opens new window)
# 接入使用
# 接口示例
先创建几个项目用于测试,创建两个默认的API项目,Api_A和Api_B,在创建一个网关项目Api_Gateway,网关项目可以选择空的模板。
现在分别在Api_A和Api_B中写几个api,将默认的WeatherForecastController中返回模型WeatherForecast添加一个字段Source,用于区分是哪个API返回的数据。
using System;
namespace Api_A
{
public class WeatherForecast
{
public string Source { get; set; } = "Api_A";
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
}
}
using System;
namespace Api_B
{
public class WeatherForecast
{
public string Source { get; set; } = "Api_B";
public DateTime Date { get; set; }
public int TemperatureC { get; set; }
public int TemperatureF => 32 + (int)(TemperatureC / 0.5556);
public string Summary { get; set; }
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
直接使用WeatherForecastController默认方法,在路由中添加api前缀。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace Api_A.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[]
{
"Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool", "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching"
};
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()
{
var rng = new Random();
return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast
{
Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index),
TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55),
Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)]
}).ToArray();
}
}
}
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
namespace Api_B.Controllers
{
[ApiController]
[Route("api/[controller]")]
public class WeatherForecastController : ControllerBase
{
private static readonly string[] Summaries = new[]
{
"Freezing", "Bracing", "Chilly", "Cool", "Mild", "Warm", "Balmy", "Hot", "Sweltering", "Scorching"
};
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<WeatherForecast> Get()
{
var rng = new Random();
return Enumerable.Range(1, 5).Select(index => new WeatherForecast
{
Date = DateTime.Now.AddDays(index),
TemperatureC = rng.Next(-20, 55),
Summary = Summaries[rng.Next(Summaries.Length)]
}).ToArray();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
再分别在Api_A和Api_B中添加两个控制器:ApiAController、ApiBController,然后加上几个简单的restful api。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Api_A.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ApiAController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public string Get(int id)
{
return $"Get:{id}";
}
[HttpPost]
public string Post([FromForm] string value)
{
return $"Post:{value}";
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public string Put(int id, [FromForm] string value)
{
return $"Put:{id}:{value}";
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public string Delete(int id)
{
return $"Delete:{id}";
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace Api_B.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class ApiBController : ControllerBase
{
[HttpGet]
public IEnumerable<string> Get()
{
return new string[] { "value1", "value2" };
}
[HttpGet("{id}")]
public string Get(int id)
{
return $"Get:{id}";
}
[HttpPost]
public string Post([FromForm] string value)
{
return $"Post:{value}";
}
[HttpPut("{id}")]
public string Put(int id, [FromForm] string value)
{
return $"Put:{id}:{value}";
}
[HttpDelete("{id}")]
public string Delete(int id)
{
return $"Delete:{id}";
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
方便查看接口,这里添加一下swagger组件,这样我们Api_A和Api_B项目分别就有了6个接口。
接着打包docker镜像,放在docker中运行这两个api项目。这一步可以用任何你熟悉的方式,run起来即可。
docker build -t api_a:dev -f ./Api_A/Dockerfile .
docker build -t api_b:dev -f ./Api_B/Dockerfile .
2
build成功后,指定两个端口运行api项目。
docker run -d -p 5050:80 --name api_a api_a:dev
docker run -d -p 5051:80 --name api_b api_b:dev
2
Api_A指定了5050端口,通过 http://localhost:5050/swagger (opens new window)打开可以看到swagger文档界面,Api_B指定了5051端口,通过 http://localhost:5051/swagger (opens new window)打开可以看到swagger文档界面,这样就大功告成了,接下来才是重点将两个api项目配置到Api_Gateway网关项目中。
# 配置网关
在网关项目Api_Gateway中都添加Ocelot组件包。
Install-Package Ocelot
Ocelot中最关键的就是配置路由信息,新建一个ocelot.json配置文件,将我们的两个API接口匹配规则放进去。
{
"Routes": [
//ApiA
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/WeatherForecast",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5050
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiA/WeatherForecast",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ]
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/ApiA",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5050
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiA",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "POST" ]
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/ApiA/{id}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5050
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiA/{id}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Put", "Delete" ]
},
//ApiB
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/WeatherForecast",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5051
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiB/WeatherForecast",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get" ]
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/ApiB",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5051
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiB",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "POST" ]
},
{
"DownstreamPathTemplate": "/api/ApiB/{id}",
"DownstreamScheme": "http",
"DownstreamHostAndPorts": [
{
"Host": "localhost",
"Port": 5051
}
],
"UpstreamPathTemplate": "/ApiB/{id}",
"UpstreamHttpMethod": [ "Get", "Put", "Delete" ]
}
],
"GlobalConfiguration": {
"BaseUrl": "https://localhost:44335"
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
关于配置文件中的各项具体含义,可以参考官方文档中的介绍。主要就是将DownstreamPathTemplate模板内容转换为UpstreamPathTemplate模板内容进行接口的访问,同时可以指定HTTP请求的方式等等。GlobalConfiguration中的BaseUrl为我们暴漏出去的网关地址。
设置好ocelot.json后,需要在代码中使用它,在Program.cs中添加配置文件。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
namespace Api_Gateway
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
CreateHostBuilder(args).Build().Run();
}
public static IHostBuilder CreateHostBuilder(string[] args) =>
Host.CreateDefaultBuilder(args)
.ConfigureAppConfiguration((context, config) =>
{
config.AddJsonFile("ocelot.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
})
.ConfigureWebHostDefaults(webBuilder =>
{
webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>();
});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
在Startup.cs中使用Ocelot。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Hosting;
using Ocelot.DependencyInjection;
using Ocelot.Middleware;
namespace Api_Gateway
{
public class Startup
{
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddOcelot();
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseRouting();
app.UseEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapGet("/", async context =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello World!");
});
});
app.UseOcelot().Wait();
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
完成以上操作后,我们试着去调用接口看看能否正确获取预期数据。
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiA"
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiB"
curl -X POST "https://localhost:44335/ApiA" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "value=ApiA"
curl -X POST "https://localhost:44335/ApiB" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "value=ApiB"
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiA/12345"
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiB/12345"
curl -X PUT "https://localhost:44335/ApiA/12345" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "value=ApiA"
curl -X PUT "https://localhost:44335/ApiB/12345" -H "Content-Type: multipart/form-data" -F "value=ApiB"
curl -X DELETE "https://localhost:44335/ApiA/12345"
curl -X DELETE "https://localhost:44335/ApiB/12345"
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiA/WeatherForecast"
curl -X GET "https://localhost:44335/ApiB/WeatherForecast"
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
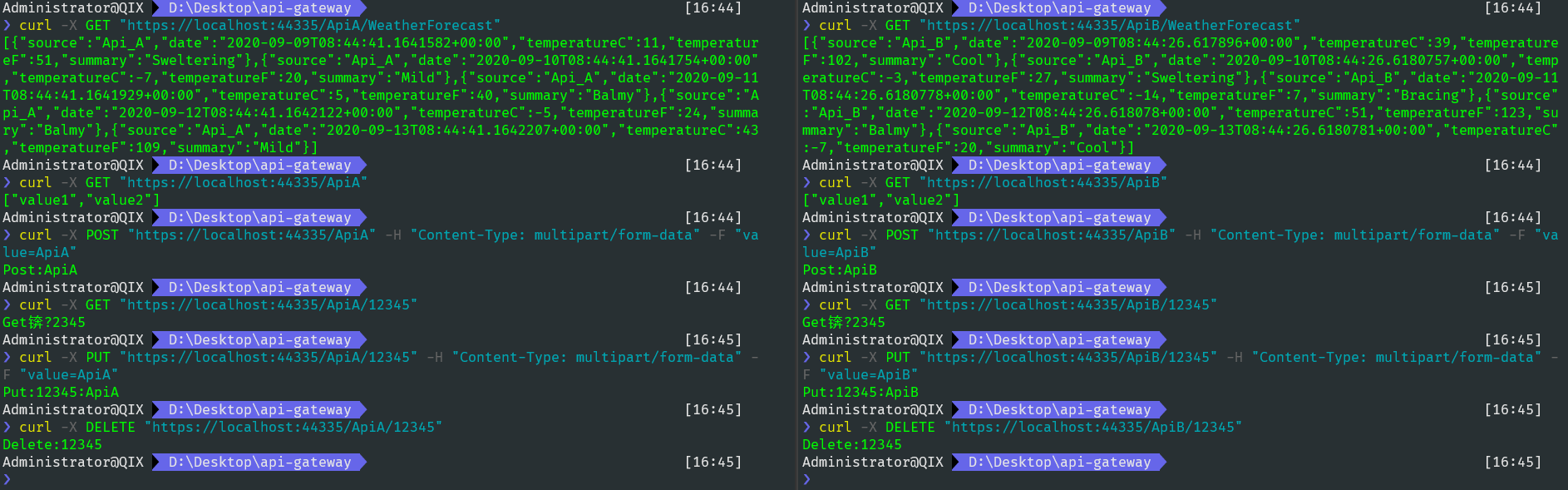
可以看到,两个项目中的接口全部可以通过网关项目暴露的地址进行中转,是不是很方便?
本篇只是简单的应用,对于Ocelot的功能远不止于此,它非常强大,还可以实现请求聚合、服务发现、认证、鉴权、限流熔断、并内置了负载均衡器,而且这些功能都是只需要简单的配置即可完成。就不一一描述了,如有实际开发需求和问题,可以查看官方文档和示例。