# .NET Core 集成JWT认证
JWT(Json web token)就不用过多的介绍了,在 .NET Core 开发中使用JWT进行认证也是比较常见的,而且接入过程也比较简单,随便配置配置就好了。
要想使用JWT,仅仅只需要在项目中引用微软的一个认证组件。
Install-Package Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authentication.JwtBearer
然后将一些敏感数据可以放在配置文件appsettings.json中。
{
"JWT": {
"ClockSkew": 10,
"ValidAudience": "https://meowv.com",
"ValidIssuer": "阿星Plus",
"IssuerSigningKey": "6Zi/5pifUGx1c+mYv+aYn1BsdXPpmL/mmJ9QbHVz6Zi/5pifUGx1c+mYv+aYn1BsdXPpmL/mmJ9QbHVz6Zi/5pifUGx1c+mYv+aYn1BsdXPpmL/mmJ9QbHVz6Zi/5pifUGx1cw==",
"Expires": 30
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
在Startup中添加配置并且使用
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
options.TokenValidationParameters = new TokenValidationParameters
{
ValidateIssuer = true,
ValidateAudience = true,
ValidateLifetime = true,
ClockSkew = TimeSpan.FromSeconds(Convert.ToInt32(Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["ClockSkew"])),
ValidateIssuerSigningKey = true,
ValidAudience = Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["ValidAudience"],
ValidIssuer = Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["ValidIssuer"],
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["IssuerSigningKey"]))
};
});
services.AddAuthorization();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
app.UseAuthentication();
app.UseAuthorization();
2
这样一个简单的JWT配置就完成了,接下来新写一个接口去生成token。
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens;
using System;
using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt;
using System.Security.Claims;
using System.Text;
namespace JsonWebTokenDemo.Controllers
{
[Route("api/[controller]")]
[ApiController]
public class AuthController : ControllerBase
{
public AuthController(IConfiguration configuration)
{
Configuration = configuration;
}
public IConfiguration Configuration { get; }
[HttpGet]
[Route("Token")]
public string GenerateTokenAsync(string username, string password)
{
if (username == "meowv" && password == "123")
{
var claims = new[] {
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Name, username),
new Claim(ClaimTypes.Email, "123@meowv.com"),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Exp, $"{new DateTimeOffset(DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(Convert.ToInt32(Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["Expires"]))).ToUnixTimeSeconds()}"),
new Claim(JwtRegisteredClaimNames.Nbf, $"{new DateTimeOffset(DateTime.Now).ToUnixTimeSeconds()}")
};
var key = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["IssuerSigningKey"]));
var creds = new SigningCredentials(key, SecurityAlgorithms.HmacSha256);
var securityToken = new JwtSecurityToken(
issuer: Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["ValidIssuer"],
audience: Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["ValidAudience"],
claims: claims,
expires: DateTime.Now.AddMinutes(Convert.ToInt32(Configuration.GetSection("JWT")["Expires"])),
signingCredentials: creds);
var token = new JwtSecurityTokenHandler().WriteToken(securityToken);
return token;
}
else
{
throw new Exception("账号密码错误");
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
模拟用户登录,成功登录则去生成token,在实际应用中还可以对接第三方登录系统进行认证,调用接口看下效果。
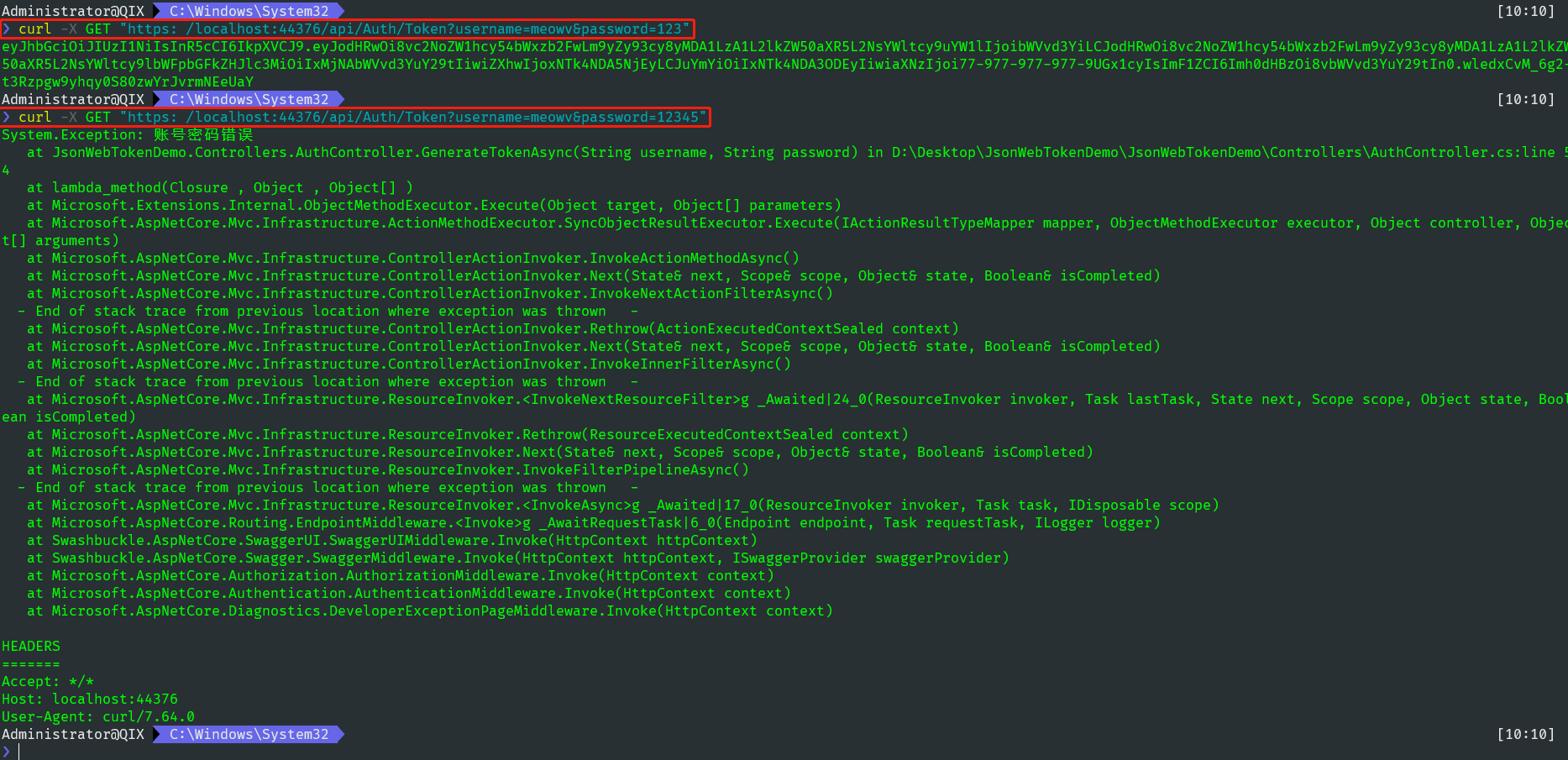
可以看到第一个接口输入正确的账号密码,成功返回了token,第二个接口会抛出一个异常。
接下来去写两个接口,去验证一下token的使用是否正常,写一个需要授权的接口和一个不需要授权的接口。
[HttpGet]
[Authorize]
[Route("AuthorizeTest")]
public string AuthorizeTest()
{
return "我是返回结果";
}
[HttpGet]
[AllowAnonymous]
[Route("AllowAnonymousTest")]
public string AllowAnonymousTest()
{
return "我是返回结果";
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这两个接口的唯一区别就是,[Authorize]、[AllowAnonymous]。
添加了 [Authorize]特性的表明是需要进行授权才可以访问此接口,而添加了[AllowAnonymous]特性则表明不需要授权谁都可以访问,同样调用看一下效果。
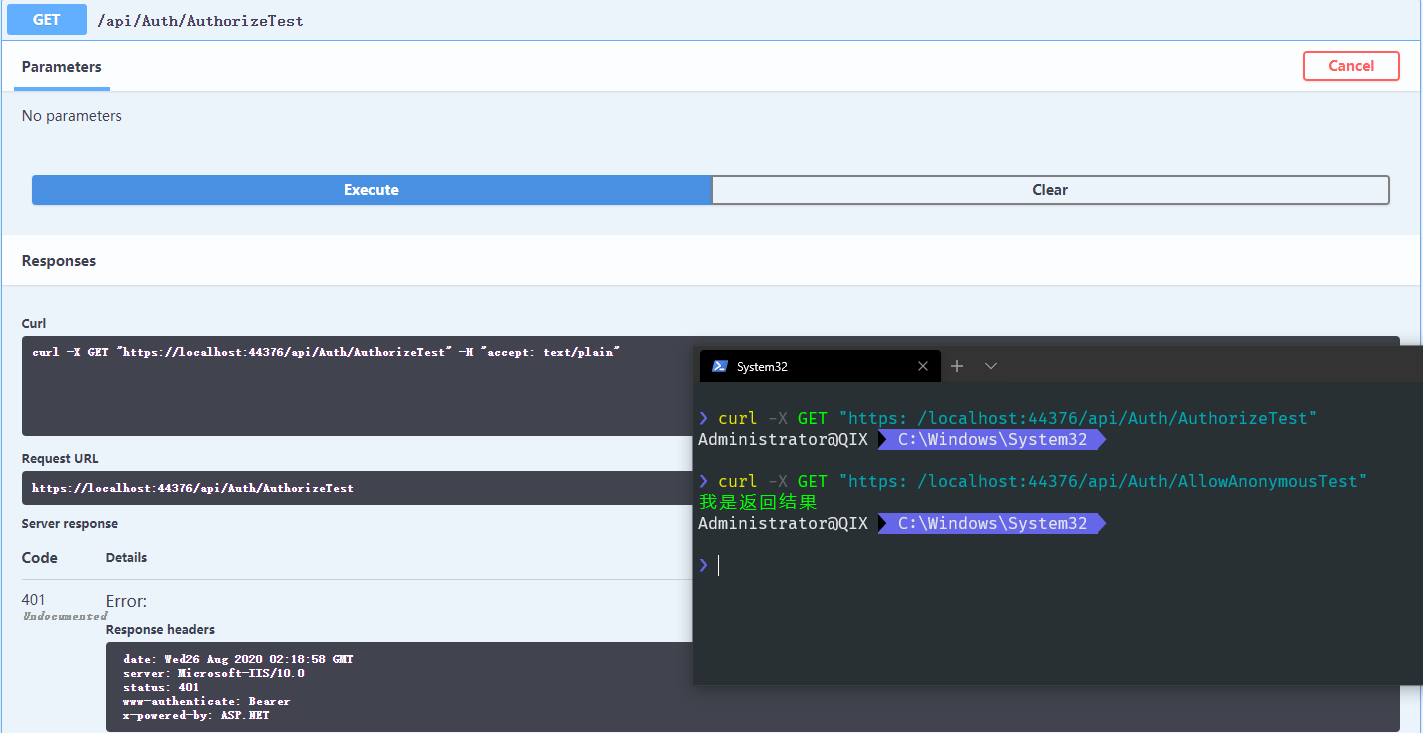
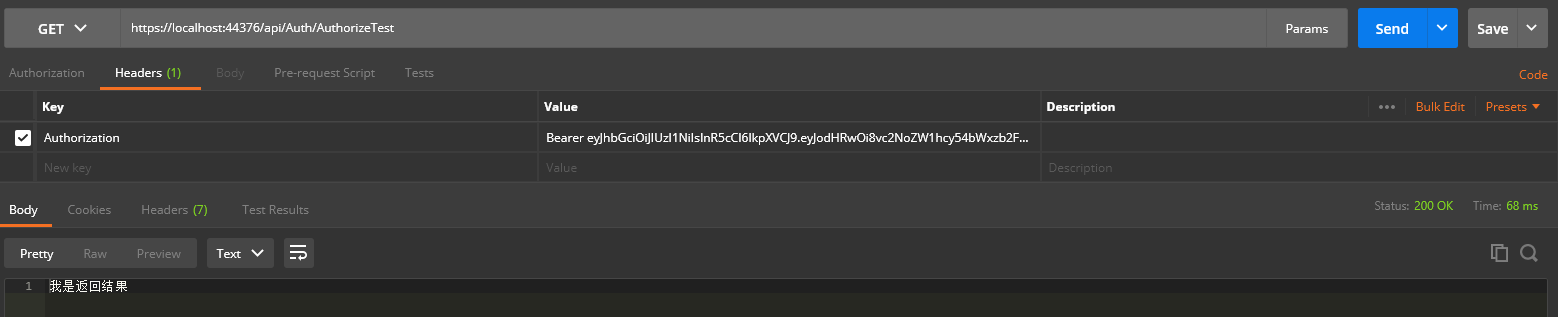
第一个接口没有返回出结果,可见生效了,此时调用的时候就需要带上我们前面生成的token成功授权后才能返回数据。
有时候当我们没有成功授权,会直接返回一个401的错误页面,如果需要自定义返回信息需要怎么做呢?
这个有好几种做法,可以用中间件,拦截器等等,不过这里推荐一种组件集成好的做法,直接上代码。
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
...
options.Events = new JwtBearerEvents
{
OnChallenge = async context =>
{
context.HandleResponse();
context.Response.ContentType = "application/json;charset=utf-8";
context.Response.StatusCode = StatusCodes.Status401Unauthorized;
await context.Response.WriteAsync("{\"message\":\"Unauthorized\",\"success\":false}");
}
};
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
添加上面这段代码即可,await context.Response.WriteAsync()可以返回你自定义的错误消息,这里返回的是一个json字符串。
另外还有一种场景,默认我们拿到token进行授权访问,是需要在请求头中添加Authorization Bearer {token}这种方式的,如果我不想在请求头中使用要怎么做呢?比如我想将token放在URL参数中,或者cookie中?
同样也是可以的,而且实现方式也超级简单,看下面代码。
services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme)
.AddJwtBearer(options =>
{
...
options.Events = new JwtBearerEvents
{
...
OnMessageReceived = async context =>
{
context.Token = context.Request.Query["token"];
await Task.CompletedTask;
}
};
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
这里演示了将token放在URL请求参数中,其它情况请根据实际开发场景进行修改即可。
